Climate Home reveals that the World Bank Group has counted support for luxury hotels as climate finance, which experts say fails the most vulnerable
The spotless white-sand beach of Le Lamantin luxury resort in Saly, about 90 kilometres south of Senegal’s capital Dakar, is lined with neat rows of sun loungers and parasols. Here, holidaymakers enjoy jet-skiing, catamaran-sailing and spa therapy, unaware that their hotel is benefiting from international climate finance channelled through the World Bank Group.
Just a few kilometres further south, however, local fishermen in Mbour, the country’s second-largest fishing port, are struggling. The beaches where they keep their boats are being progressively eaten away by rising seas that also threaten their homes.
The stark contrast between the neighbouring coastal areas highlights how global funding for climate projects – largely taxpayers’ money from rich countries – often fails to help those shouldering the burden of warming impacts, especially when it is being used to mobilise more private investment for green aims.
“They prioritise Saly because the hotels are wealthy,” said Saliou Diouf, a retired fisherman who lost his house in Mbour to encroaching waves. “The World Bank should help the most vulnerable.”
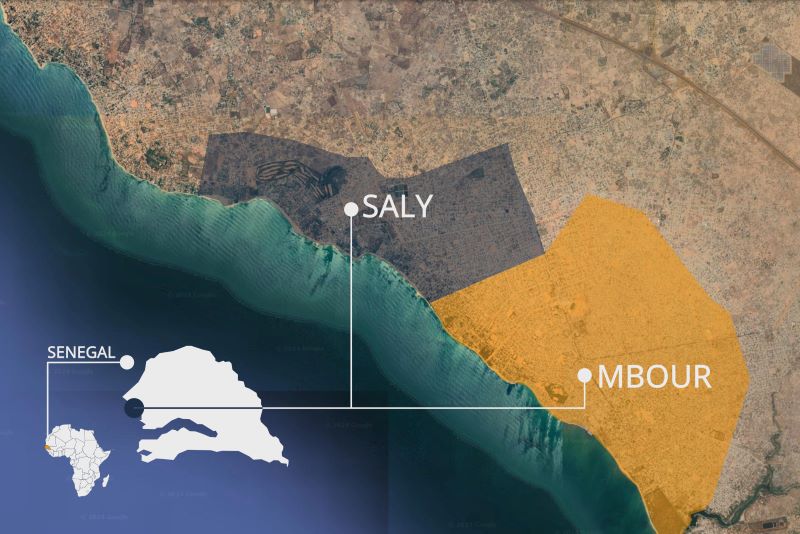
Map showing the location of the neighbouring communities of Saly and Mbour on Senegal’s coast (Graphic: Fanis Kollias)
Le Lamantin is one of a dozen upscale hotels in sub-Saharan Africa acquired by Mauritius-based Kasada Hospitality Fund LP – whose investors are Qatar’s sovereign wealth fund and multinational hotel giant Accor – which it is revamping in accordance with EDGE, a green building certification created by the World Bank.
Kasada was granted over $190 million in guarantees by the World Bank Group’s Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA), and loans of up to $160 million by its private-sector lender, the International Finance Corporation, to help it snap up hotels across Kenya, Nigeria, Ivory Coast, Rwanda, Namibia and Senegal, and spruce them up as Accor brands like Mövenpick.
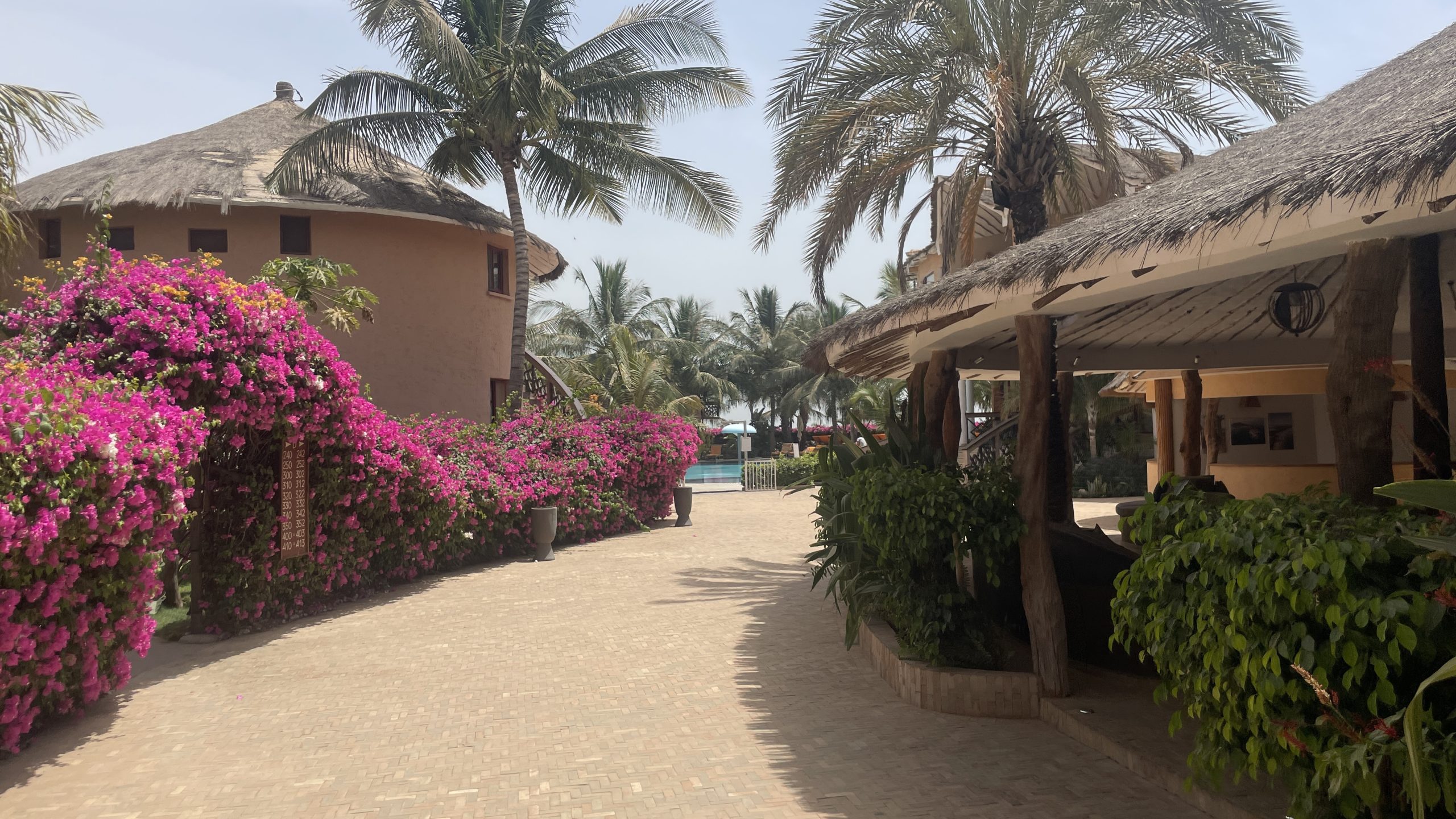

The Mövenpick Resort Lamantin Saly, where a standard hotel room costs about £220 a night (Photo: Jack Thompson)
MIGA, the little-known insurance arm of the World Bank Group, has counted its backing for the hotels as part of its climate efforts for the past three years, according to annual sustainability reports.
The five-star resort in the West African nation of Senegal, where rooms cost at least £220 a night ($270), is being refurbished to consume at least 20% less energy and water than other comparable buildings by its owner Kasada, which expects it to obtain EDGE certification this year.
Teresa Anderson, global lead on climate justice for ActionAid International, told Climate Home it is “shocking that what little funds there are for climate action are benefiting luxury hotels”.
“Climate finance must be used to help those most vulnerable – not to help the world’s wealthiest add a climate hashtag to their Instagram posts by the pool,” she said.
MIGA told Climate Home its support for Kasada is primarily aimed at developing Senegal’s tourism sector and creating jobs, adding that refurbishing hotels can also have beneficial climate impacts and play an important role in decarbonising the hospitality industry.
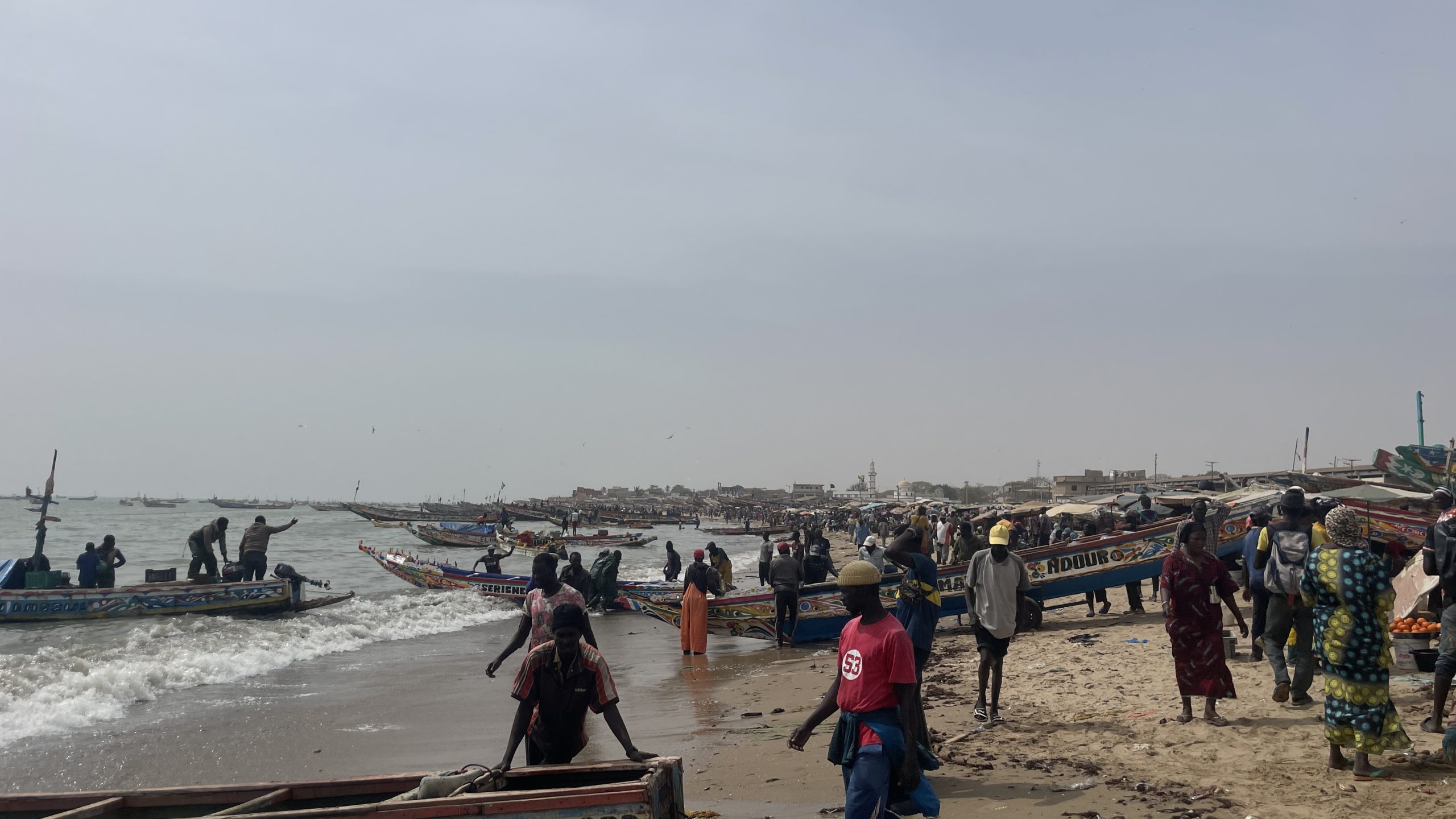

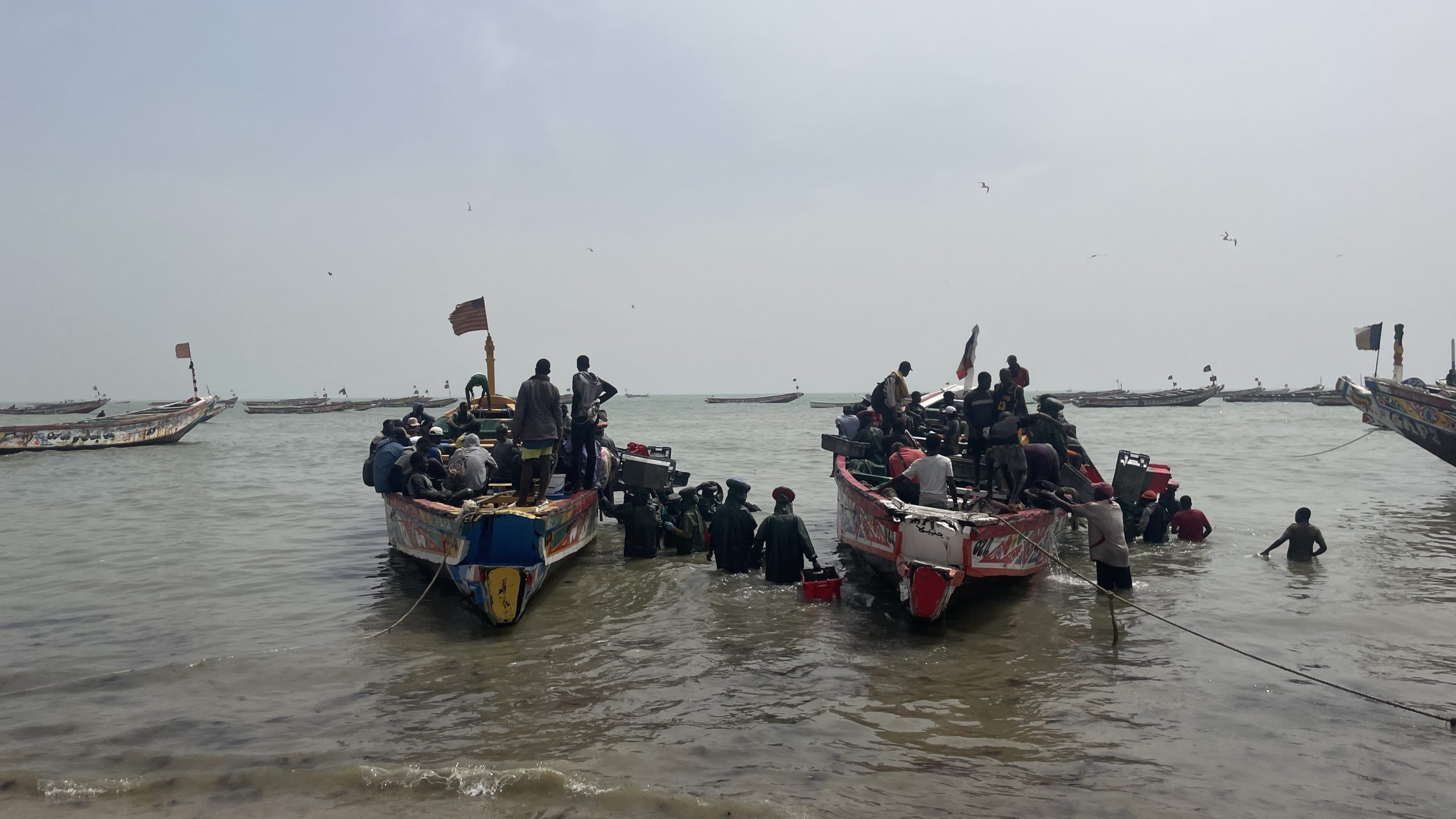
Mbour, just a few miles from the pristine beaches of Saly, is the second-largest fishing hub in Senegal with 11,000 fishers. (Photo: Jack Thompson)
‘The money is missing’
In nearby Mbour, however, the fishing community feels left behind.
“I was born here, I grew up here – when I was a child, the sea only came up to the last pole,” Diouf told Climate Home, pointing to the remnants of a Portuguese-built pontoon used to moor colonial ships in the 1800s.
In just one generation, he said, the sea has gobbled up more than 100 metres of beach in Mbour, forcing 30 families to abandon their houses and threatening hundreds more. A quarter of the Senegalese coastline – home to 60% of the population – is at high risk of erosion.
Mbour’s fast-disappearing shore is a crisis for its 11,000 fishers as big swells destroy their boats, crammed into the remaining patch of sand.
But in Saly, it’s a different story. Here, between 2017 and 2022, under a separate project, the World Bank invested $74 million in beach protection, building 19 stone walls, groynes and breakwaters to reclaim 8-9 kilometres of hotel-lined beachfront, popular with tourists.
The World Bank Group said the project helped preserve around 15,000 direct and indirect jobs by saving tourism infrastructure, while also protecting two fishing villages in Saly.
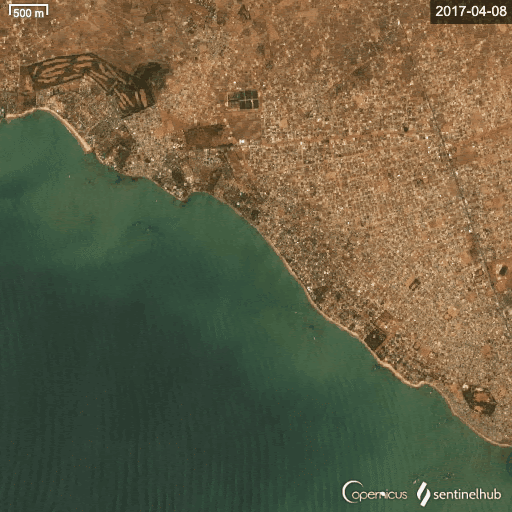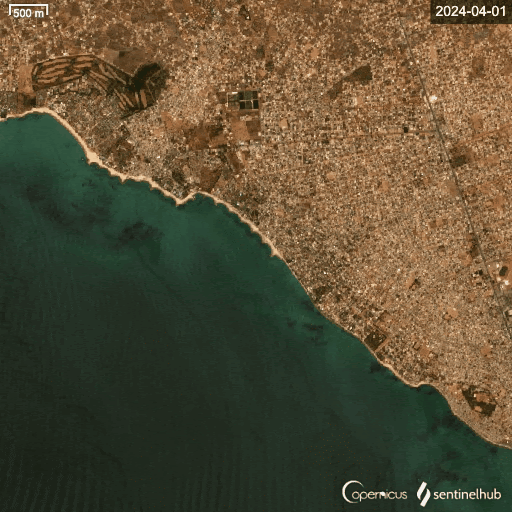
Satellite data shows the changing coastline in Saly (north), where protective infrastructure was developed, and Mbour (south), which has none. (Photo: Modified Copernicus Sentinel data [2024]/Sentinel Hub)
Kasada told Climate Home, meanwhile, that Le Lamantin hotel has so far created about 50 direct jobs of different types for people living near Saly, with MIGA also pointing to indirect employment stimulated by the resort such as agriculture, handicrafts and transport.
The World Bank Group (WBG) said its units work together to avoid trade-offs. “It’s not to either support hotels and the tourism sector as a driver of development, or to enhance the resilience of local communities – the WBG does both,” it said in a written response to Climate Home.
But fishermen in Mbour – which was outside the scope of the Saly coastal protection infrastructure project – are not benefiting from that approach, and even say the works in Saly have exacerbated erosion in their area. The Mbour artisanal fisheries council has devised a climate adaptation strategy to address the problem.
One of its coordinators, Moustapha Senghor, said seawalls and breakwaters are needed, but there are no funds for what would amount to “a colossal investment”. “We know exactly what we need to do, but the money is missing,” he said.
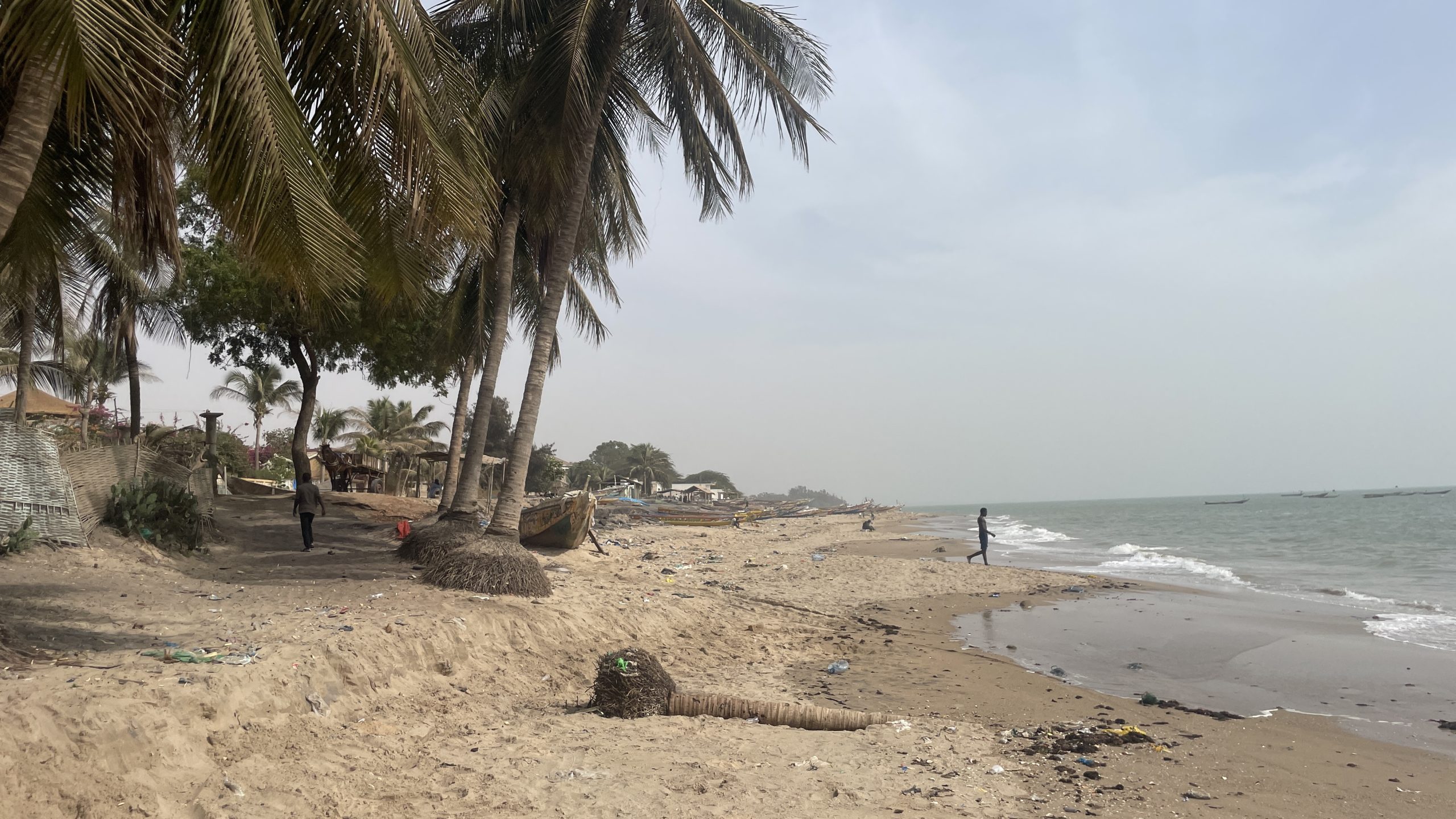

Sea level rise is threatening beach-side homes and swallowing coconut trees that protect the coastline in Mbour, Senegal. (Photo: Jack Thompson)
Private-sector trillions
Governments and climate justice activists are putting pressure on the World Bank to significantly step up its role in funding climate projects, especially to help the most vulnerable countries and communities.
For the past three years, a group of countries led by Barbados’ Prime Minister Mia Mottley has called for reforms so that the bank can better address climate change.
At the same time, wealthy nations have been reluctant to inject more capital into its coffers, while attempts at tinkering with the balance sheet to squeeze out more climate cash only go so far.
For World Bank Group President Ajay Banga, the real solution lies in greater private-sector involvement, using scarce public money as a lever to help mobilise huge dollar sums for climate and development goals this decade.
“We know that governments and multilateral institutions and philanthropies all working together will still fall short of providing the trillions that we will require annually for climate, for fragility, for inequality in the world. We therefore need the private sector,” Banga told media ahead of this week’s annual Spring Meetings of the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund.
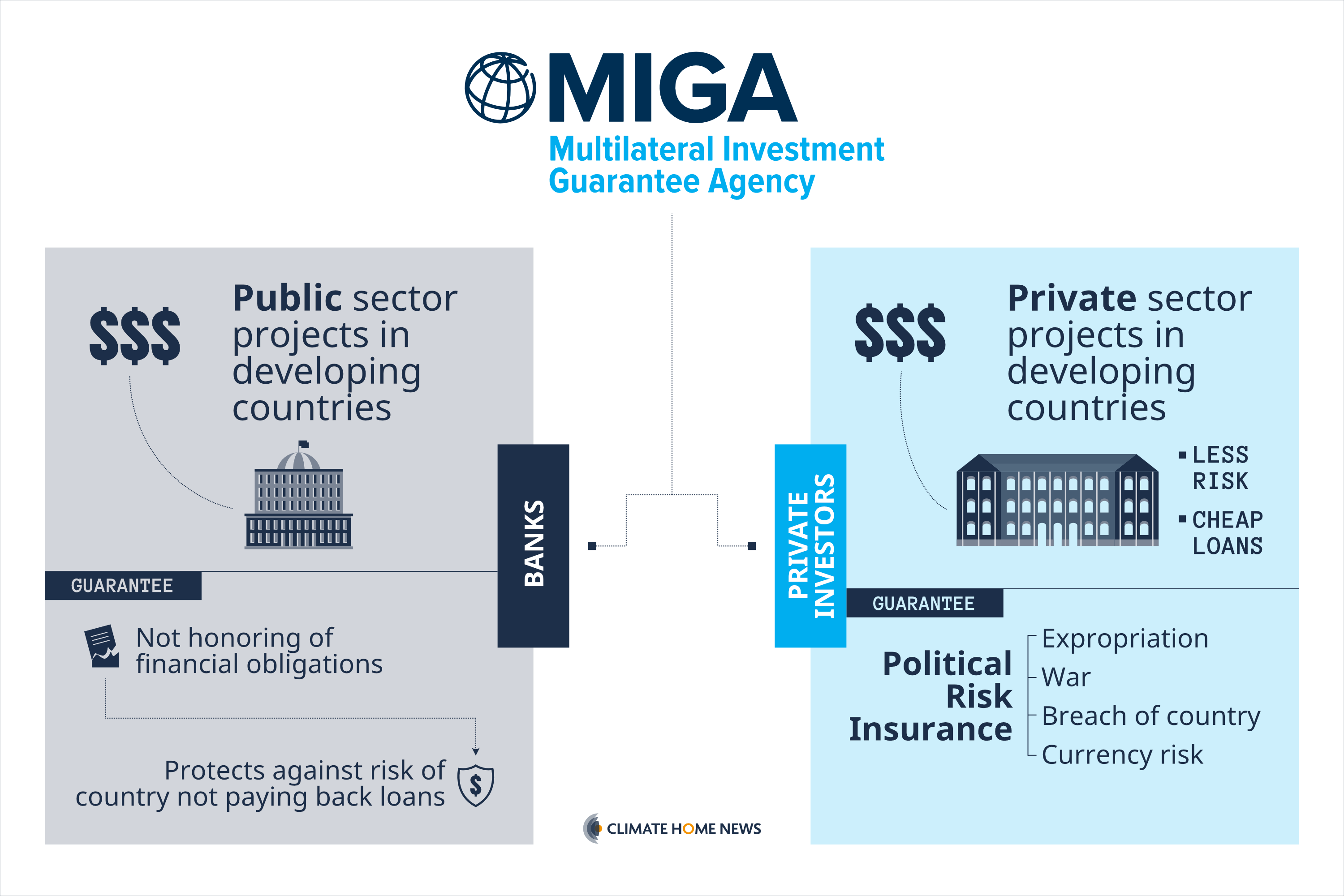
MIGA’s guarantees can be a key driver of climate investments in developing countries. (Graphic: Fanis Kollias)
Following suggestions from a group of CEOs convened by Banga, the World Bank Group announced in February a major overhaul of its guarantee business to enable “improved access and faster execution”. The goal is to triple issuances, including those from MIGA, to $20 billion by 2030, with a significant proportion of that expected to support green projects.
MIGA – as a provider of guarantees aimed at encouraging private capital into developing countries – may not be the obvious choice to help low-income communities like Mbour’s fishers.
But, in its 2023 sustainability report, the agency wrote: “because the poorest are the most vulnerable to climate change, MIGA is working to mobilize more private finance to scale up climate adaptation, resilience and preparedness”.
Last year, less than one percent of MIGA’s total guarantees directly supported climate adaptation measures, according to its annual report.
The guarantees generally act as a form of political risk insurance, making an investment less risky and giving companies access to cheaper loans as a result.
MIGA’s 2023 sustainability report showcases the Kasada-owned hotels as an example of its efforts to “rapidly ramp up” private capital for climate action, with the agency providing its highest volume of climate finance last year.
Struggle to fund adaptation
But some experts argue the World Bank Group should be targeting its efforts more closely on communities who are struggling to survive as global warming exacerbates extreme weather and rising seas.
Vijaya Ramachandran, a director at the Breakthrough Institute, a California-based environmental research centre, said projects like the Kasada-backed hotels are “not where the dollars are best spent from a climate perspective”.
Ramachandran, a former World Bank economist, co-authored a study last year analysing the climate portfolio of the bank’s public-sector lending arms, which exclude MIGA. It found a lack of clarity over what constitutes a climate project and showed that hundreds of projects had been tagged as climate finance despite having little to do with emissions-reduction efforts or adaptation.
Ramachandran told Climate Home that, in the case of MIGA’s backing for the African hotels, Kasada “should just be doing the energy saving itself as part of its own efforts to address climate change”.
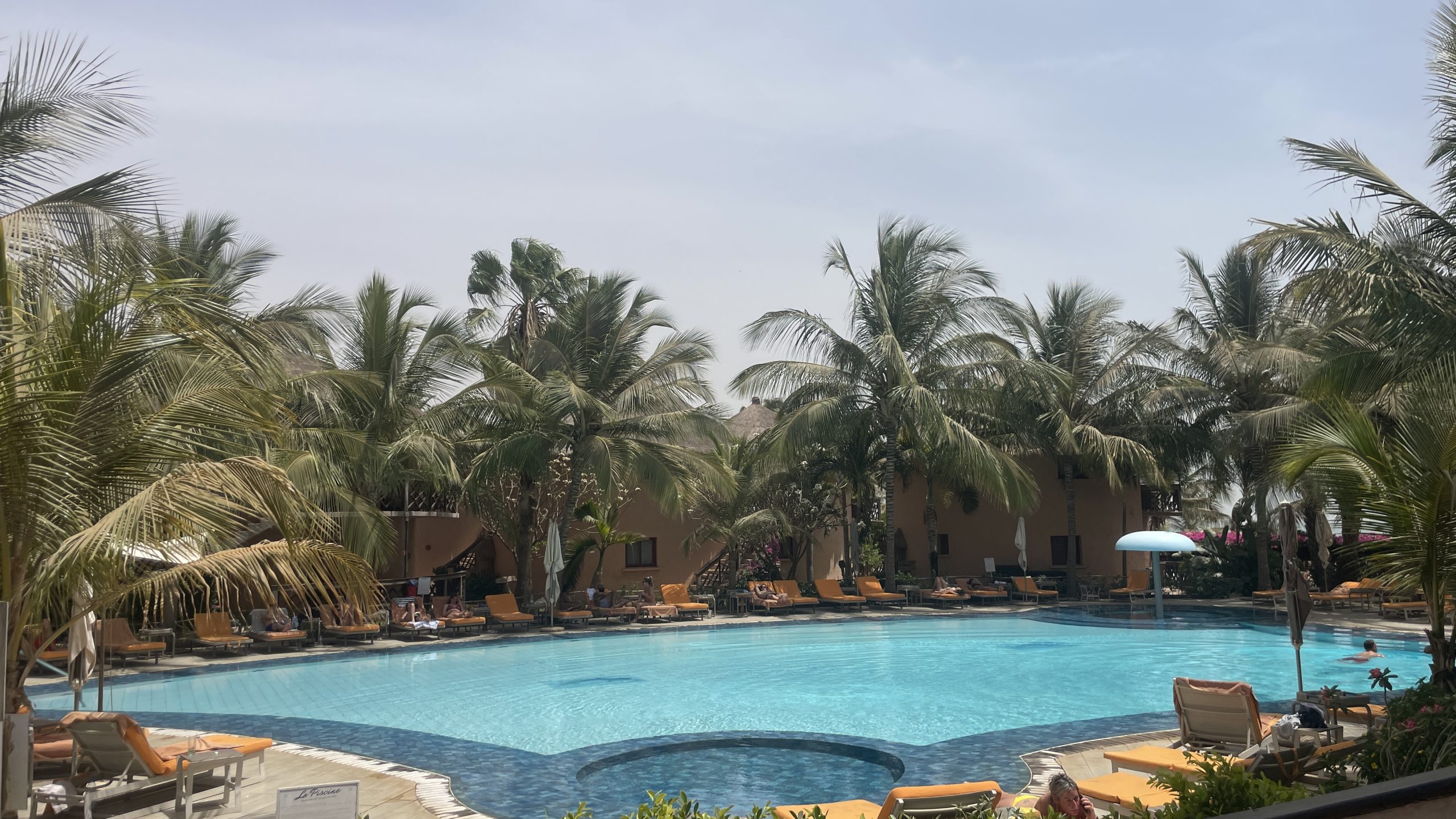

Holidaymakers enjoy a spacious, ocean-side pool at the five-star Le Lamantin resort in Saly, Senegal. (Photo: Jack Thompson)
Olivier Granet and David Damiba, managing partners of Kasada Capital Management, told Climate Home the hotel investment fund had always planned to be “a leader in energy and water efficiency in its properties”.
But, they added, the financial and technical support of MIGA and the IFC had helped them implement their strategy “further and more easily”, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eight Kasada-owned hotels have already been certified under EDGE and the rest are expected to achieve the standard this year, they noted.
Ramachandran said making hotels energy-efficient is a good thing – “but from a public finance perspective, for poorer African countries the focus should be on adaptation and making them more resilient”.
Around the world, measures to help people adjust to the devastating impacts of climate change, from fiercer floods and drought to sea-level rise, have been chronically underfunded.
Developing countries need an estimated $387 billion a year to carry out their current adaptation plans, but in 2021 they received only $24.6 billion in international adaptation finance, according to the latest figures published by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
MIGA to miss climate target?
Once regarded by campaigners as the “World Bank’s dirtiest wing” for its support of fossil fuels, MIGA has come under mounting pressure to shift its subsidies in a greener direction, in line with broader institutional goals.
In response, the agency has committed to throw more of its financial weight behind projects that aim to cut greenhouse gas emissions or alleviate the impacts of climate change.
In 2020, it revealed a plan to dedicate at least 35% of its guarantees to climate projects on average from fiscal year 2021 through 2025, embracing a target set by the wider World Bank Group.
MIGA conceded at the time this would be “a challenge” – and it now looks likely to fall short of the goal. In 2023, climate finance represented 28% of its guaranteed investments.
According to the agency’s 2023 sustainability report, 31 out of 40 projects it supported with guarantees last year had a climate mitigation or adaptation component, but it did not disclose what percentage of each was counted as climate finance.
Meanwhile, over the last three years, MIGA has backed three gas-fired power plants in Mozambique and Bangladesh, while it is also planning to support an additional one in Togo.
In monetary terms, MIGA’s annual provision of climate guarantees has risen from just over $1 billion in 2019 to $1.5 billion in 2023, pushing up the total size of its climate portfolio to $8.4 billion. But the headline numbers only paint a partial picture, clouded by a lack of transparency in the data.
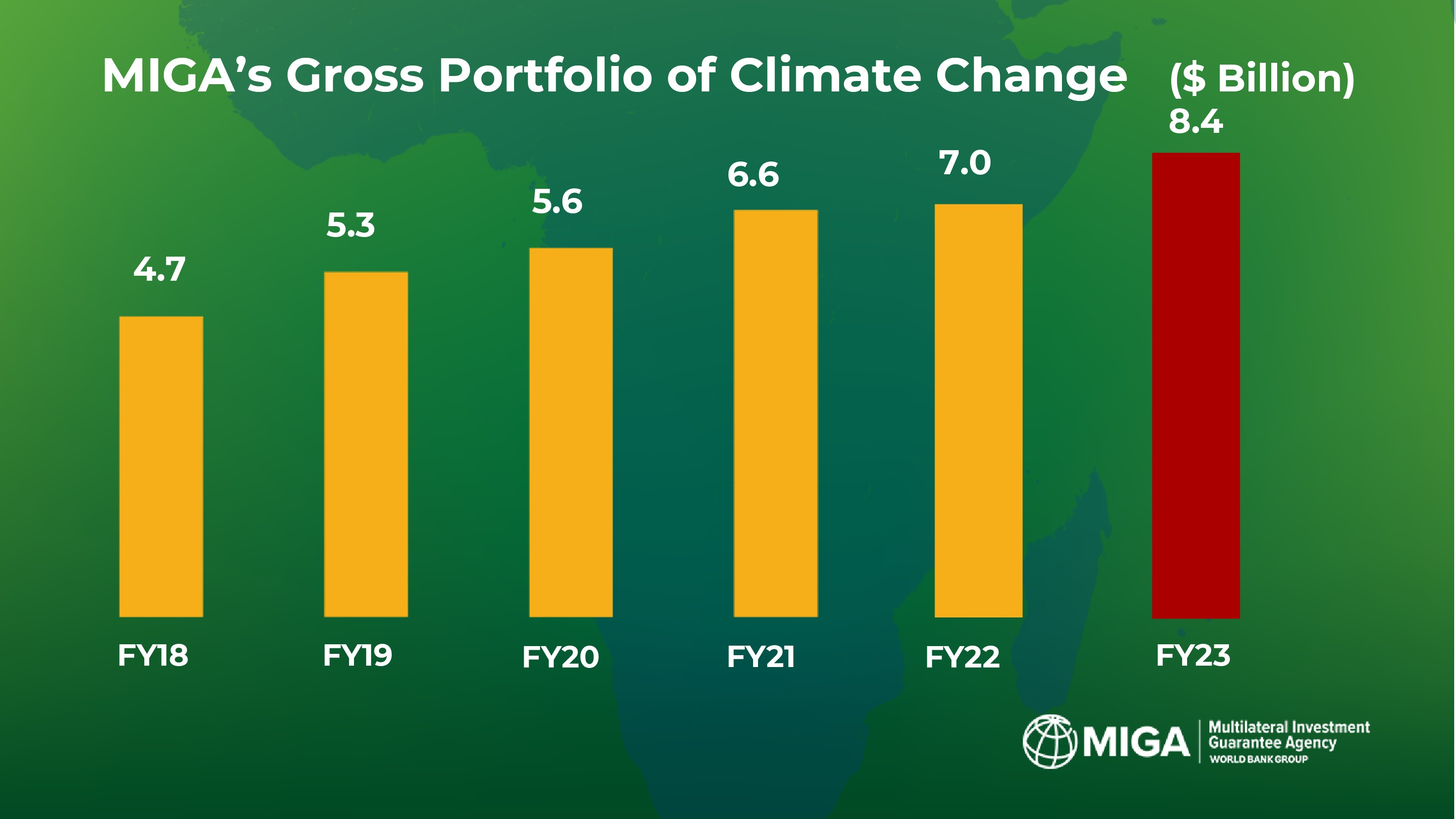
MIGA’s portfolio of climate investments has grown in the past six years. (Photo: MIGA Climate Change)
In response to Climate Home’s request for a full list of MIGA’s climate projects, the agency said it could not disclose the information for confidentiality reasons.
“Our clients are private-sector investors or financiers, and we do not have agreement to release disaggregated information about their investments and financing,” a MIGA spokesperson said.
The only clues about the make-up of MIGA’s climate portfolio come in its glossy annual sustainability reports, which highlight a handful of initiatives.
Climate Home News reviewed these reports from the last three available years – 2021, 2022 and 2023 – and tracked highlighted projects, which are framed as positive examples of climate finance.
Motorways and elite universities
Read More







Never miss a story. Join us on social.