While Brazil and Colombia saw forest loss drop, their progress was offset by rises elsewhere
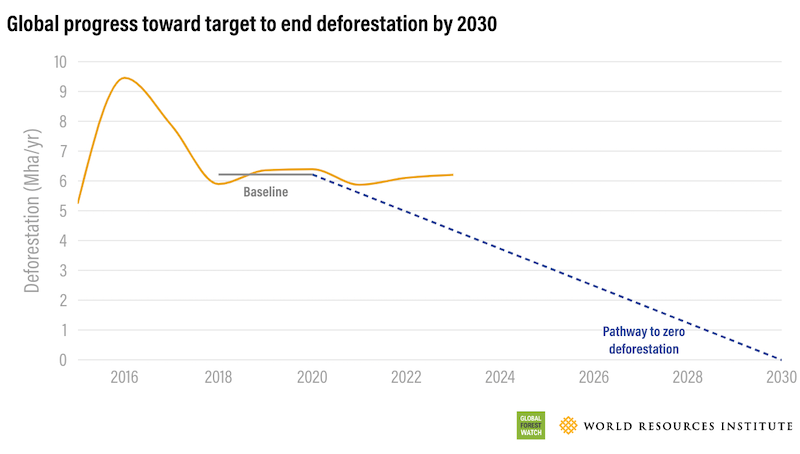
Tropical forests continued disappearing at a “stubbornly” high rate last year, putting a global goal to end deforestation by 2030 “far off track”, new research shows.
The equivalent of ten football pitches of tropical forests – 3.7 million hectares – were lost every minute in 2023 as the result of human activities and natural disasters, according to analysis carried out by Global Forest Watch.
While forest destruction slowed dramatically in Brazil and Colombia, this was offset by sharp increases in Bolivia, Nicaragua and Laos.
“The world took two steps forward, two steps back when it comes to this past year’s forest loss”, said Mikaela Weisse, Global Forest Watch Director at the World Resources Institute (WRI).
Tropical forests are one of the world’s best defenses against global warming, as they absorb greenhouse gases. But they are also where over 96% of human-made deforestation occurs worldwide, according to WRI.
Missing targets
While total tree loss in the tropics decreased slightly last year, analysts estimated human-caused deforestation driven by agriculture, commodities extraction and urban expansion continued rising.
That’s despite a 10% reduction being needed every year to meet a pledge to “halt and reverse forest loss and land degradation by 2030” signed by 145 countries, including large forest nations like Brazil, Indonesia and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Initially introduced as part of a voluntary commitment by governments at Cop26 in Glasgow, the target was mentioned for the first time in a Cop decision at last December’s climate summit in Dubai.
Weisse said the goal “has always been an ambitious one” and “it will certainly be difficult” to ensure enough progress from all countries to meet the target.
“I still find a lot of hope in the fact that Brazil, Colombia, and Indonesia have managed to massively curb their rates of forest loss in recent years”, she added. “Those countries have demonstrated how critical it is to have strong political will to combat deforestation”.
Lula’s deforestation busting
Brazil continued to be the country that lost the most tropical forest in 2023 because of the size of its immense rainforests. But its losses dropped by more than a third last year, reaching the lowest level since 2015.
Progress in Brazil coincided with the return to office of President Luiz Lula da Silva. In his first full year in the post, he strengthened law enforcement against illegal loggers, revoked anti-environmental measures introduced by his predecessor, Jair Bolsonaro, and extended Indigenous rights.
Brazil is planning to put the protection of forests at the heart of its climate summit in 2025, which is set to take place in Belém, known as the gateway to the Amazon rainforest.
“Holding Cop30 in the heart of the forest is a powerful reminder of our responsibility to keep the planet within our 1.5°C target”, said Marina Silva, Minister for the Environment and Climate Change, last December.
In neighbouring Colombia, the rate of tree loss dropped by half in 2023, primarily as a result of policies introduced by President Gustavo Petro.
Forest protection is among the goals being negotiated by the leftist government with armed groups as part of wider efforts to bring “total peace” and end decades of violence.
Experts have also suggested that criminal groups have taken it upon themselves to rein in illegal logging as a way to strengthen their hand in the discussions.
Progress lost
But positive developments in forest conservation in Brazil and Colombia have been all but cancelled out by tree losses spiralling out of control elsewhere.
In Bolivia, forest losses remained at record-breaking levels for a third year in a row, driven by uncontrolled expansion of soybean and beef production and exacerbated by exceptional wildfires.
The government, which has prioritised development and agricultural exports over forest protection, has not joined the 2030 pledge.
It was at loggerheads with Brazil at the Amazon Summit last year, when it opposed the inclusion of any references to the target in an outcome document signed by the leaders of eight countries.
Dramatic upticks in deforestation were also seen in Nicaragua, in Central America, and Laos, in South-East Asia, l
Read More